The Seoul Subway, locally known as “수도권 전철”, serves the capital of South Korea.
Inaugurated on 15 of August of 1974, This system is one of the largest and most efficient in the world, con 18 lines and 767 stations covering 940 kilometres (584 miles).
Seoul Subway Schedule
The Seoul Metro operates daily from 5:30 a.m. until the 1:00 a.m., facilitating constant movement in the metropolis.
Official websites
- For more details, visit the Seoul Subway official website.
- To see the best of seoul, The Tiqets website is the most famous about this city (and available in several languages). It also allows you to buy cheaper tickets and save yourself from waiting in line..
Seoul Subway Fares
- Single ticket price varies from 1250 a 2150 KRW (aproximadamente entre 0,94 USD y 1,62 USD), depending on the distance traveled.
- Rates for children and young people: There are significant discounts for children and young people, who can register a transportation card and benefit from reduced fares.
- Early hour discounts: Using a transportation card, passengers traveling before 6:30 a.m. can enjoy a 20% off.
Standard rates
Fares for traveling on the Seoul Metro vary depending on the distance traveled. The base price within the first 10 kilometers is 1,250 KRW. For distances between 10 y 50 kilometres, a supplement is added 100 KRW cada 5 kilometres. Beyond the 50 kilometres, the supplement fits 100 KRW cada 8 kilometres. These rates apply whether you use a transportation card or buy a single ticket.
Discounts for children and youth
There are significant discounts for children and young people, who can benefit from reduced fares when registering a transportation card. These discounts make the system more accessible for families and students, encouraging the use of public transport from an early age.
Descuentos por “Viaje temprano”
The Seoul Subway fare system includes a discount of 20% for passengers traveling before 6:30 a.m. This incentive is designed to encourage riders to travel during off-peak hours., helping to decompress demand during the most congested hours.
Special rates
For passengers who travel frequently, There is a card option with a fixed price of 61,600 KRW that allows up to 44 travel within the Seoul metropolitan area. This option is advantageous for regular travelers, as it offers considerable savings compared to purchasing single tickets for each trip.
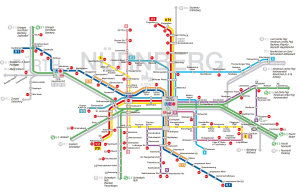
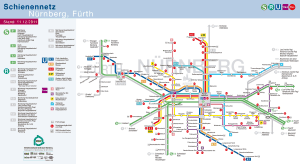
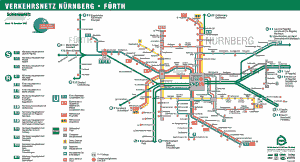
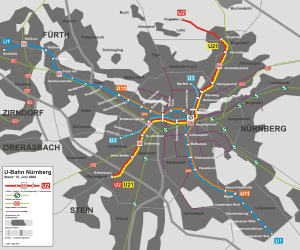
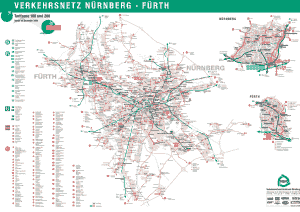
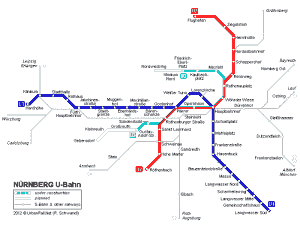
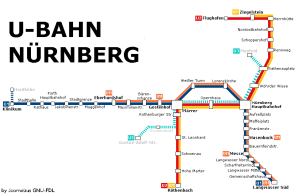
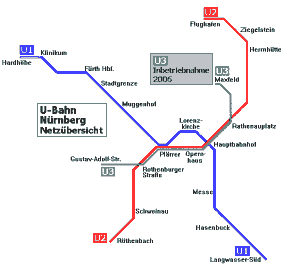
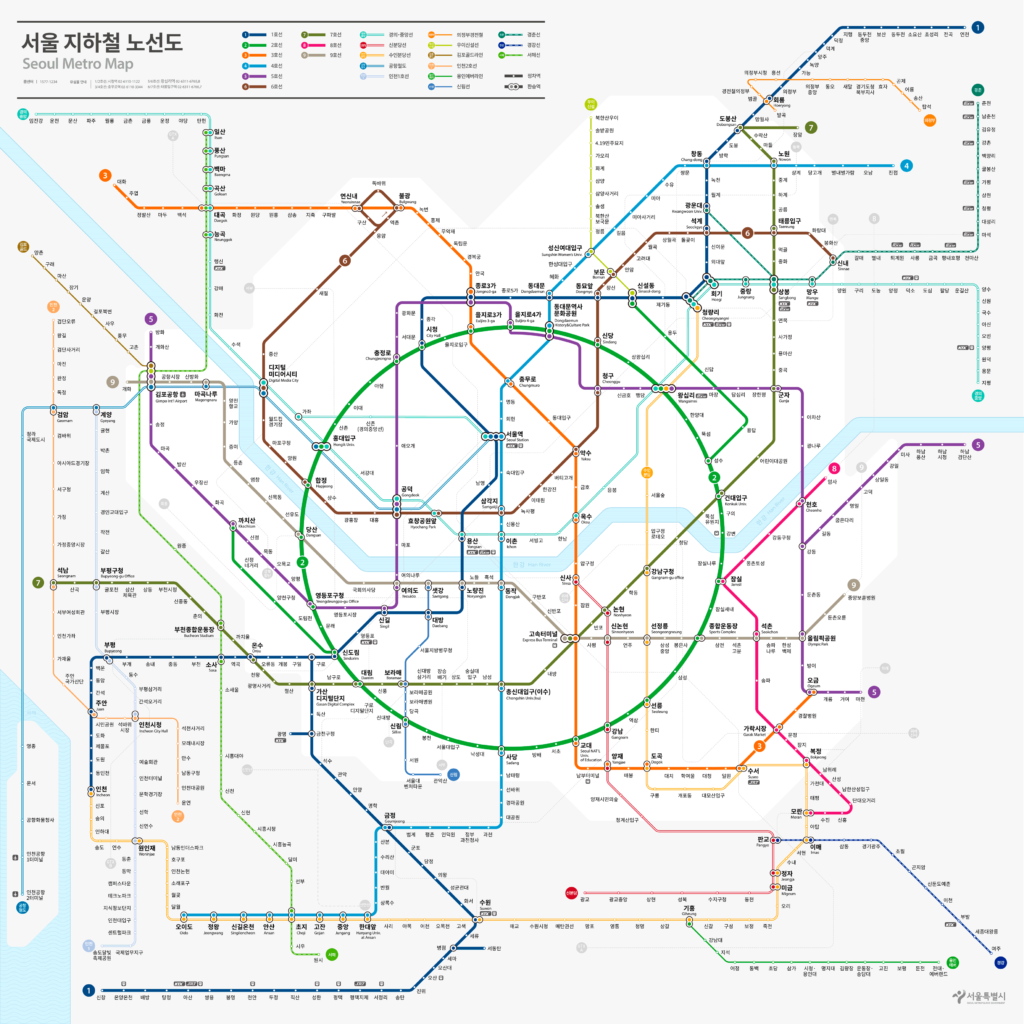
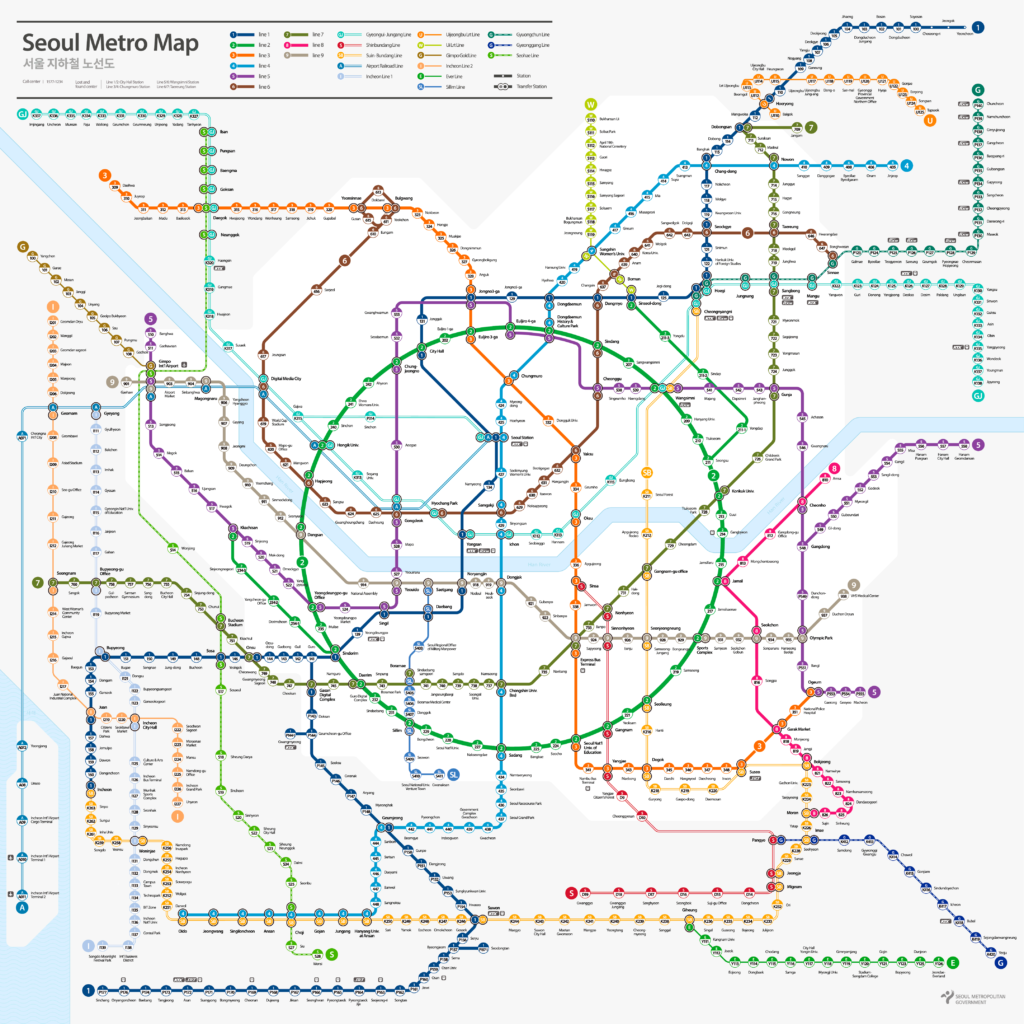
Seoul Subway Map
Below we show you the Seoul Subway map in three different languages..
Maps in Korean language:
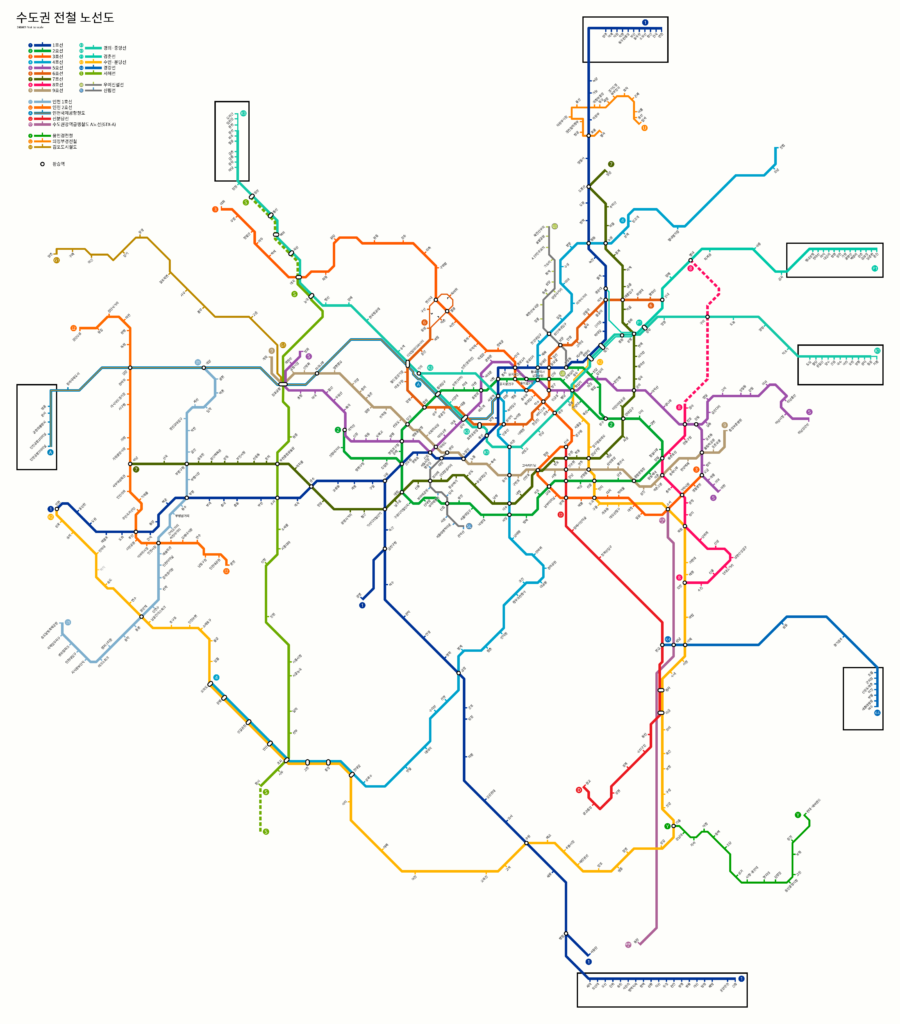
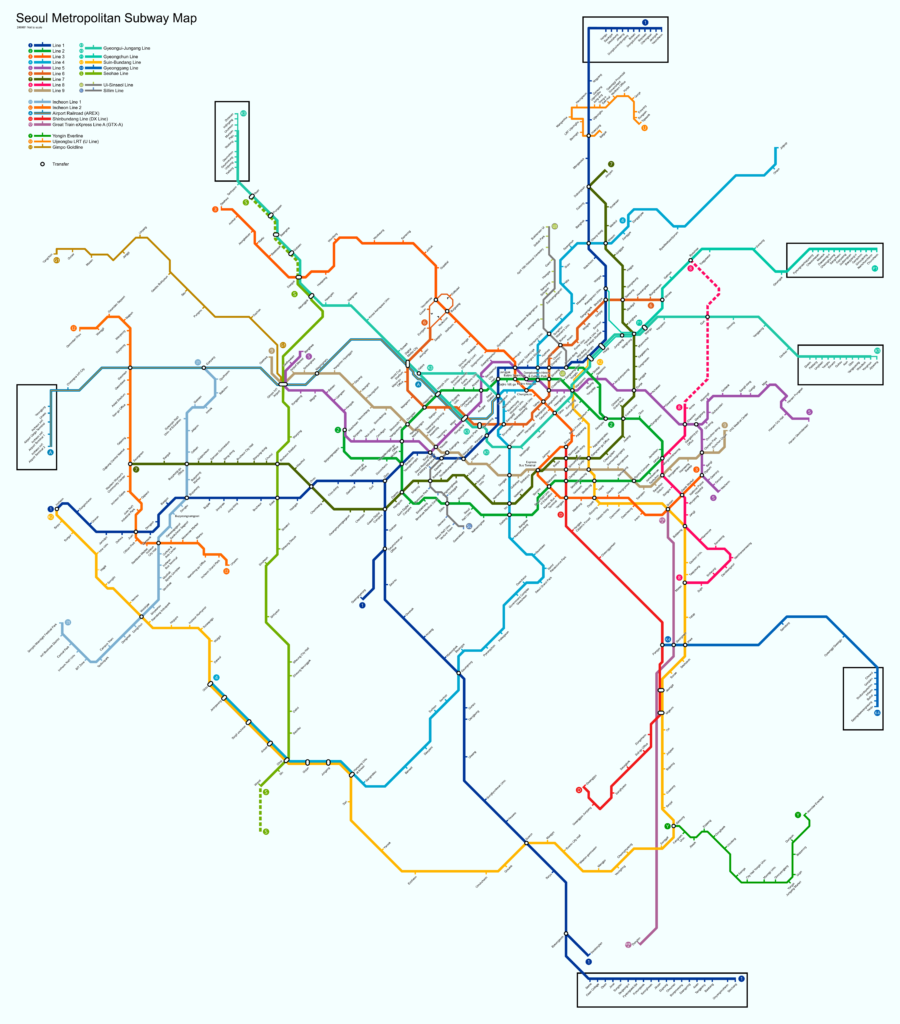
The following is the same map but with the format that existed before the year 2023:
Maps in English language:
the same map, but in the old year format 2023.
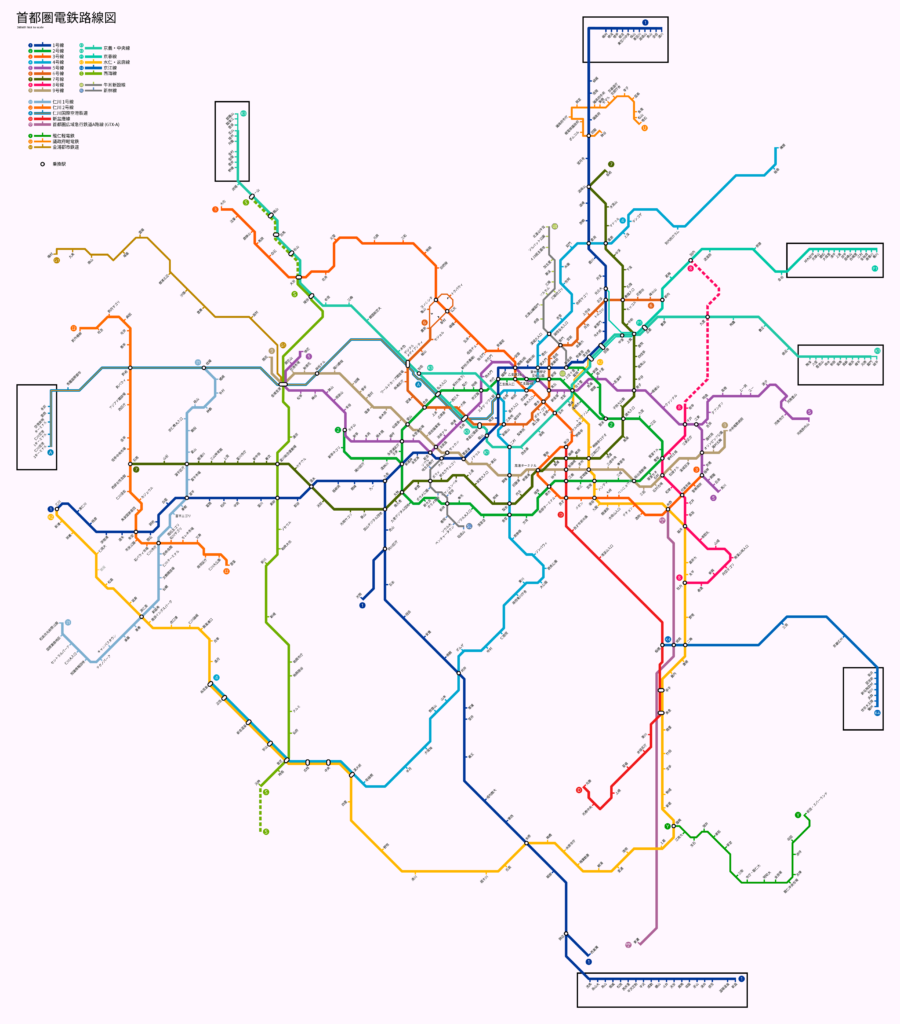
Map in Japanese language:
History of the subway
Seoul Subway, inaugurated on 15 of August of 1974, started with the Line 1, an infrastructure that revitalized transportation in the South Korean capital. This system has been developed in response to the growing demand for mobility in one of the most densely populated cities in the world..
Since its conception, The metro has played a crucial role in urban modeling and city planning, influencing the location of new residential and commercial areas.
Seoul subway expansion did not stop with the first lines. In the decade of 1980, lines were added to the metro 2, 3 y 4, while the following decades saw the introduction of lines using advanced technology, such as driverless trains and automatic platform doors to improve passenger safety. The integration of these technological advances has placed the Seoul Metro in a leading position worldwide in terms of efficiency and safety..
The most recent line, the line 9, was inaugurated in 2009 and its last extension was completed in 2021. This line is particularly notable for its express service which significantly reduces travel time between the east and west of the city..
Seoul Subway Map History
The evolution of the Seoul Subway map is a testament to its increasing expansion and complexity. The original design was relatively simple, designed to facilitate understanding of the first four lines. As the system expanded, the map was transformed into a more detailed and aesthetically attractive tool.
One of the significant changes to the map design was the introduction of distinctive colors and iconic symbols for each line in the years 90, making it easier to navigate through the system for locals and tourists alike.
Designers like Kim Hyun-Suk have played a crucial role in modernizing the map, ensuring that as new lines and stations were added, the map remained accessible and easy to use.
The latest map redesign was done to include the Line 9 and its extensions, using a more digital approach that allows integrating real-time updates and facilitating interaction with users through mobile applications and interactive screens at stations.
Additional data
The Seoul Metro is not only crucial for the daily lives of its citizens but also for tourists. Some of the sites accessible via the subway include:
- Palacio Gyeongbokgung (Gyeongbokgung Station, Line 3): A jewel of Joseon architecture, It is one of the largest and probably the most beautiful palaces in Seoul.
- Dongdaemun Market (Dongdaemun History Station & Culture Park, Lines 2, 4 y 5): A large shopping complex known for its cutting-edge fashion and local crafts.
- Torre N Seoul (Myeong-dong Station, Line 4): Offers panoramic views of the city from its location atop Mount Namsan.
- Insadong neighborhood (Anguk Station, Line 3): Famous for its art shops and traditional cafes, It is an essential place to experience Korean culture.
- Lotte World Tower (Jamsil Station, Lines 2 y 8): South Korea's tallest skyscraper offers a panoramic view of the city from its observation deck. Its facilities also include a luxurious shopping center and various entertainment attractions..
- Bukchon Hanok Village (Anguk Station, Line 3): This picturesque neighborhood offers an immersion in Korean tradition and history with its well-preserved Hanok houses. It is ideal for history buffs and those seeking an authentic cultural experience.
- Hang Park (Yeouinaru Station, Line 5): This sprawling park along the Han River is a popular picnic spot, sports activities and simply to enjoy the tranquility away from the urban hustle and bustle. The park is also famous for its open-air festivals and concerts..
- Hongdae (Hongik University Street) (Hongik University Station, Line 2): Known for its vibrant artistic and youthful atmosphere, this area offers a wide range of coffees, stores, art galleries and clubs. It is the preferred meeting place for young people and the heart of Seoul's underground entertainment.
- COEX Mall (Samseong Station, Line 2): One of the largest underground shopping malls in Asia, COEX Mall houses a wide variety of stores, a giant aquarium and the famous K-Pop Hall of Fame, making it a must-see destination for fans of Korean pop culture.
- War Memorial of Korea (Samgakji Station, Lines 4 y 6): This museum and monument commemorates South Korea's fallen in various conflicts, mainly the Korean War. It is a place of deep historical and educational reflection.
- Myeongdong Shopping Street (Myeong-dong Station, Line 4): Famous for its fashion stores, cosmetics and its varied gastronomic offer, especially street food, Myeongdong is a paradise for shoppers and those who want to experience modern Korean urban culture.
Each of these sites can be a starting point to explore the city of Seoul, all accessible through its extensive metro network.